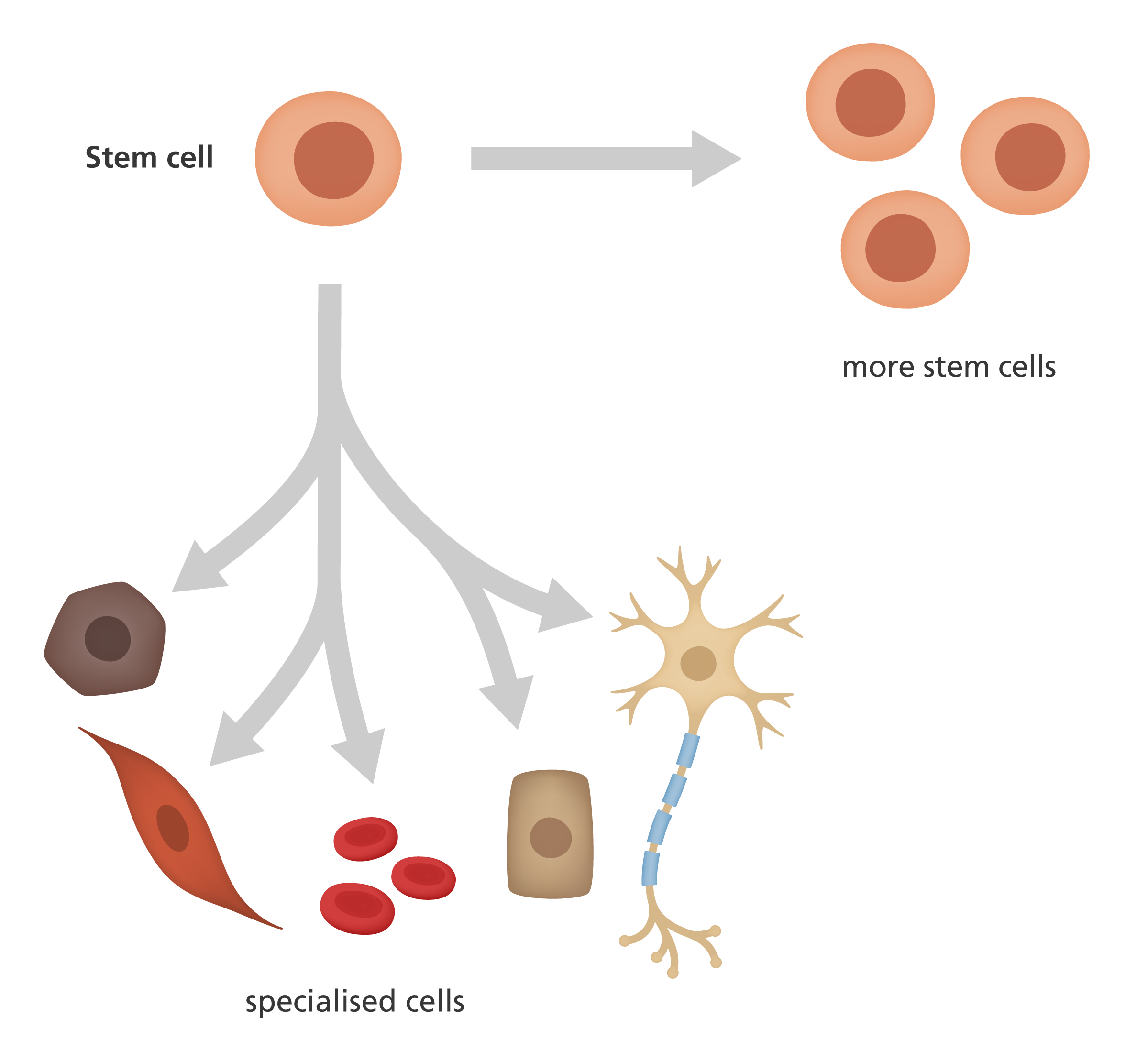
Dividing stem cells stock illustration Illustration of life Biology Diagrams An asymmetric cell division produces two daughter cells with different cellular fates. This is in contrast to symmetric cell divisions which give rise to daughter cells of equivalent fates. Notably, stem cells divide asymmetrically to give rise to two distinct daughter cells: one copy of the original stem cell as well as a second daughter programmed to differentiate into a non-stem cell fate. Cell division - AQA Stem cells. Chromosomes carry genetic information in a molecule called DNA. A type of cell division called mitosis ensures that when a cell divides each new cell produced has Collectively, both types of cell division are referred to as asymmetric cell division. An asymmetric cell division is defined as any division that gives rise to two sister cells that have different fates—a feature that can be recognized by differences in size, morphology, gene expression pattern, or the number of subsequent cell divisions undergone by the two daughter cells (Horvitz and

Stem cells and asymmetric cell division. The roles of asymmetric cell division in stem-cell control, coupled with the mechanisms that regulate this process, have been extensively reviewed 1,2,3,4
Asymmetric Stem Cell Division: Precision for Robustness Biology Diagrams
Asymmetric cell division (ACD) produces two daughter cells with distinct fates or characteristics. Many adult stem cells use ACD as a means of maintaining stem cell number and thus tissue homeostasis. Here, we review recent progress on ACD, discussing conservation between stem and non-stem cell systems, molecular mechanisms, and the biological meaning of ACD.
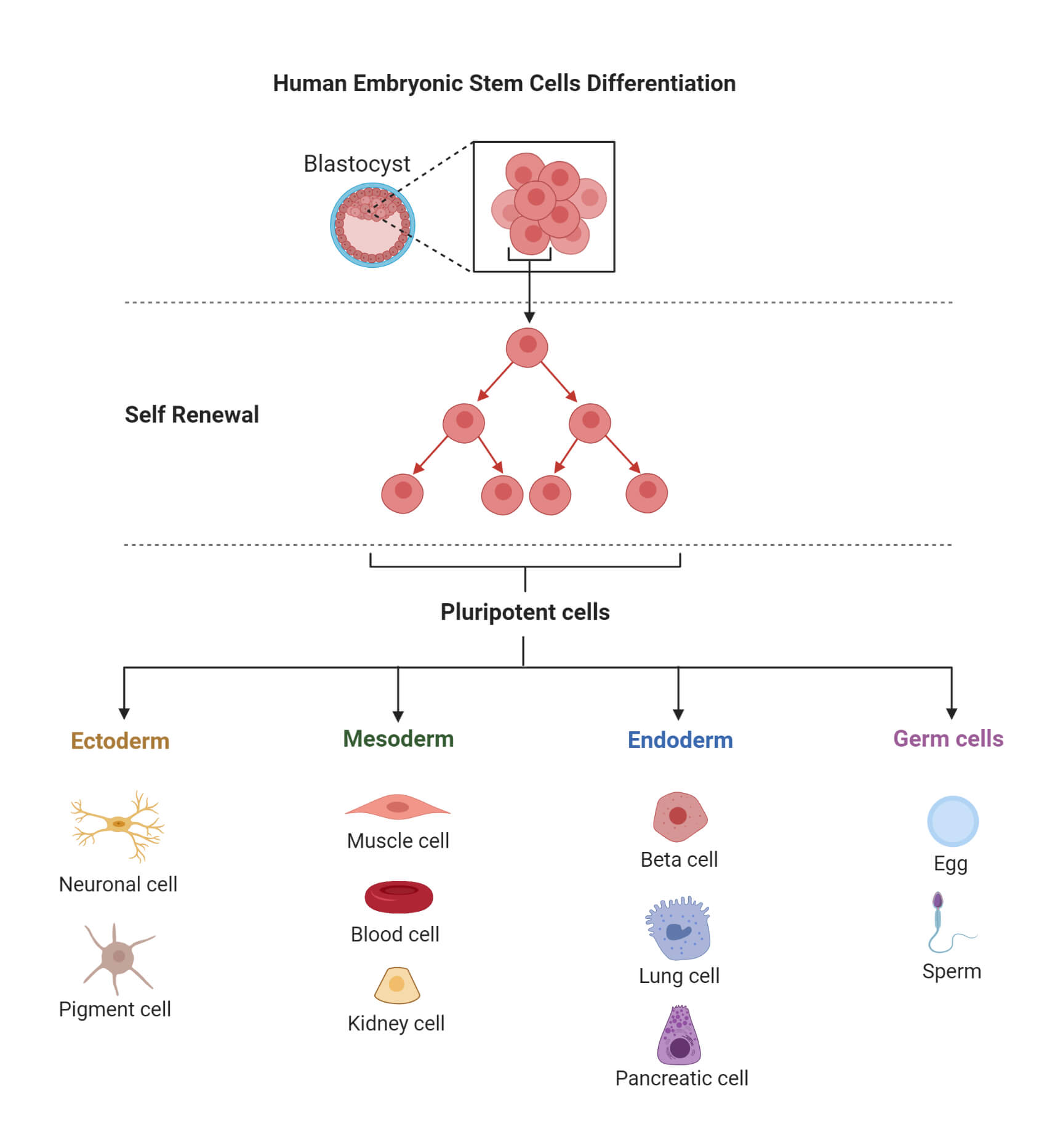
Learn about the different types of stem cells, their unique properties, and how they are cultured and differentiated in the laboratory. Find out how pluripotent stem cells can self-renew and form all the cell types of the body.

Asymmetric division of stem cells and its cancer relevance Biology Diagrams
Stem cell division decision trees for the numerical algorithm. Open in a new tab (a) Divisions of wild-type stem cells. (b) Divisions of mutant stem cells. Stem cells are denoted by light circles with an "S" and TA cells by shaded circles with a "D". One-hit mutants are marked with a star.