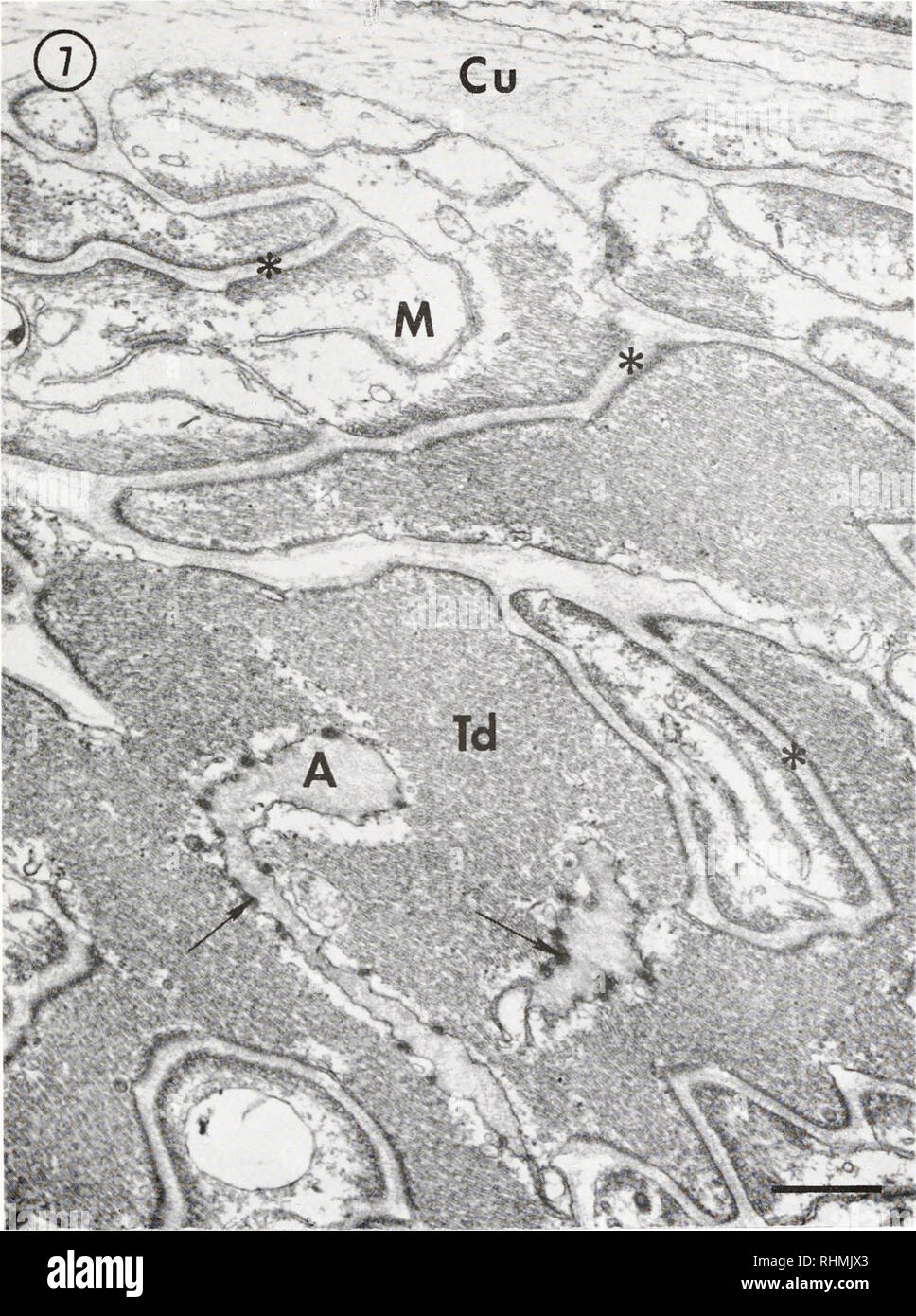
Myotendinous junction Biology Diagrams sipates stress at the junction between the relatively soft tendon and the hard bone and thereby reduces peak stress. The myo-tendinous junction is a highly specialised region where collagen fibrils are inserted deep into recesses formed by myocytes. This arrangement allows transmission of tension forces across the tendon and muscle interface.1 Tendinous portion. The tendinous portion is made up of multidirectional collagen fibres. but rather in the body of the muscle cells just proximal to the MTJ. Hjort M, Hansen KK, Qvortrup K, Kjaer M, Krogsgaard MR. The human myotendinous junction: an ultrastructural and 3D analysis study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015 Feb;25(1):e116-23 The musculotendinous junction is the point where the muscle pierces the tendon. The osteotendinous junction is the point where the tendon inserts on the bone. Cell Population and the Extracellular Matrix. Tenocytes and tenoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that coexist in tendinous tissue. Tenocytes are elongated, while tenoblasts are ovoid.

Connexin 43 is situated in gap junctions between cells in rows along the collagen fibres. Connexins 26 and 32 have a more diffuse pattern. Each tendon will differ throughout the body depending on the rate in which they are strained. The behaviour of the collagen within the tendon depends on the intramolecular types, quantity and bond.
Anatomy, Tendons Biology Diagrams
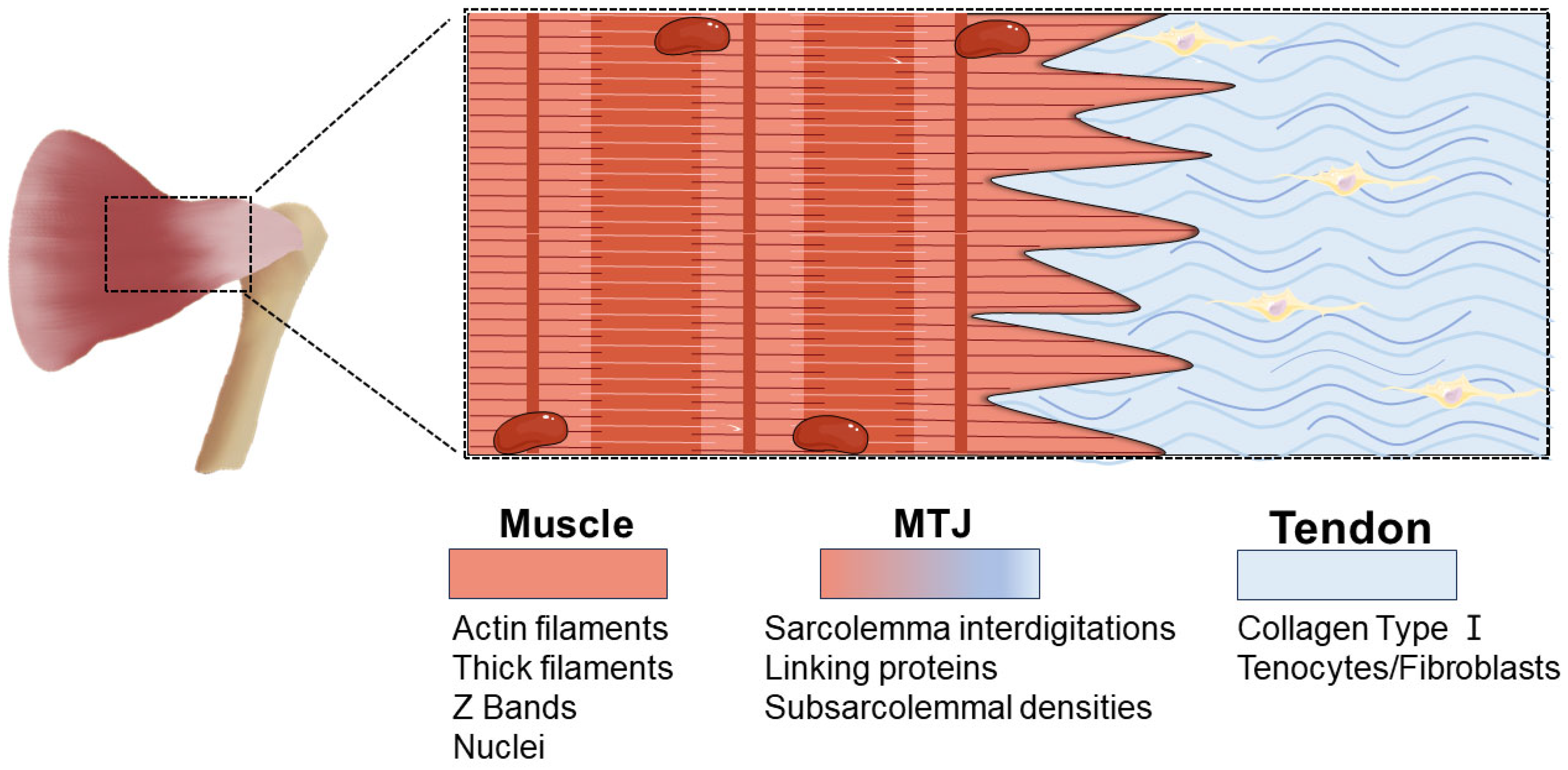
The muscle-tendon junction (MTJ) is a highly specific tissue interface where the muscle's fascia intersects with the extracellular matrix of the tendon. The MTJ functions as the particular structure facilitating the transmission of force from contractive muscle fibers to the skeletal system, enabling movement. Considering that the MTJ is continuously exposed to constant mechanical forces

The myotendinous junction (MTJ) is a specialized structure in the musculotendinous system, where force is transmitted from muscle to tendon. Animal models have shown that the MTJ takes form of tendon finger-like processes merging with muscle tissue. The human MTJ is largely unknown and has never been described in three dimensions (3D).

PDF Tendon and ligament: basic science, injury and repair Biology Diagrams
Musculotendinous junction (MTJ): The point where the tendon attaches to your muscle. Note this is a frequent site of injury. Osteotendinous junction (OTJ): The point where the tendon attaches to your bone. The Sharpey fibers that are part of the tendon extend into the bone.
The ultimate part of the treatment plan involves elevating the wounded body part above the level of the heart, which can effectively reduce swelling. Since inflammation is a pivotal feature of the body's reaction to muscle injury caused by stretching, the most commonly accepted therapy is nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).