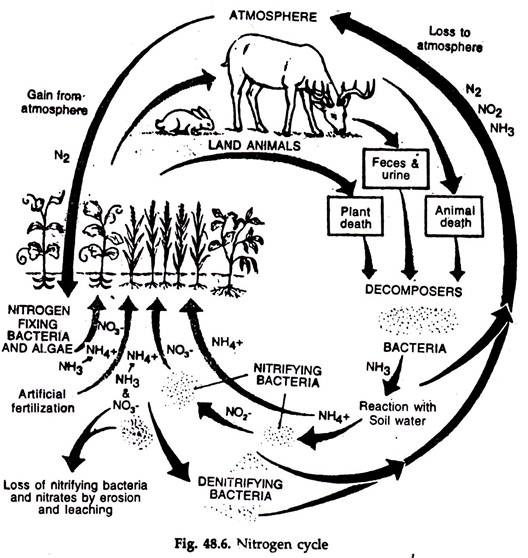
STPL World of Biology 13 Food Chain Biology Diagrams Without the nitrogen cycle, the synthesis of vital organic compounds would be hindered, leading to a collapse in the food chain and ecosystem dynamics. Stages of Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Fixation: Nitrogen gas (N₂) in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia (NH₃) or related nitrogenous compounds in soil and water, primarily by nitrogen When herbivores consume plants, and predators consume herbivores, this nitrogen is then transferred through the food chain. H3 Denitrification: Returning Nitrogen to the Atmosphere. Denitrification completes the nitrogen cycle, returning fixed nitrogen back to the atmosphere as nitrogen gas (N2). Under anaerobic conditions, such as waterlogged

Nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process which transforms inert atmospheric nitrogen to a usable form for plants, animals and other organisms. Login. Organic nitrogen exists in living organisms, and they get passed through the food chain by the consumption of other living organisms.
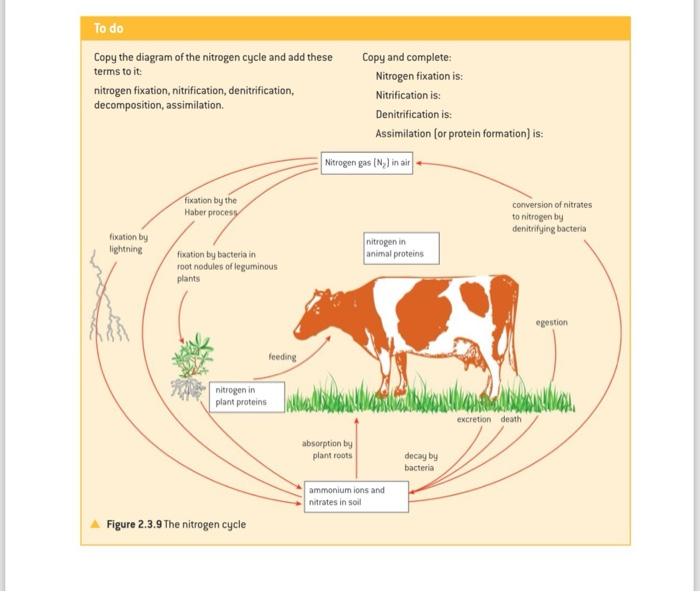
Steps And Significance Biology Diagrams
Stage three of the nitrogen cycle. Moving along food chains and excretion. Image caption, Stage four of the nitrogen cycle. Death of animals. Image caption, Stage five of the nitrogen cycle. The movement of nitrogen between the atmosphere, biosphere, and geosphere in different forms is called the nitrogen cycle and is one of the major biogeochemical cycles. It may also be considered as the movement of nitrogen through the food chain from simple inorganic compounds, mainly ammonia, to complex organic compounds.
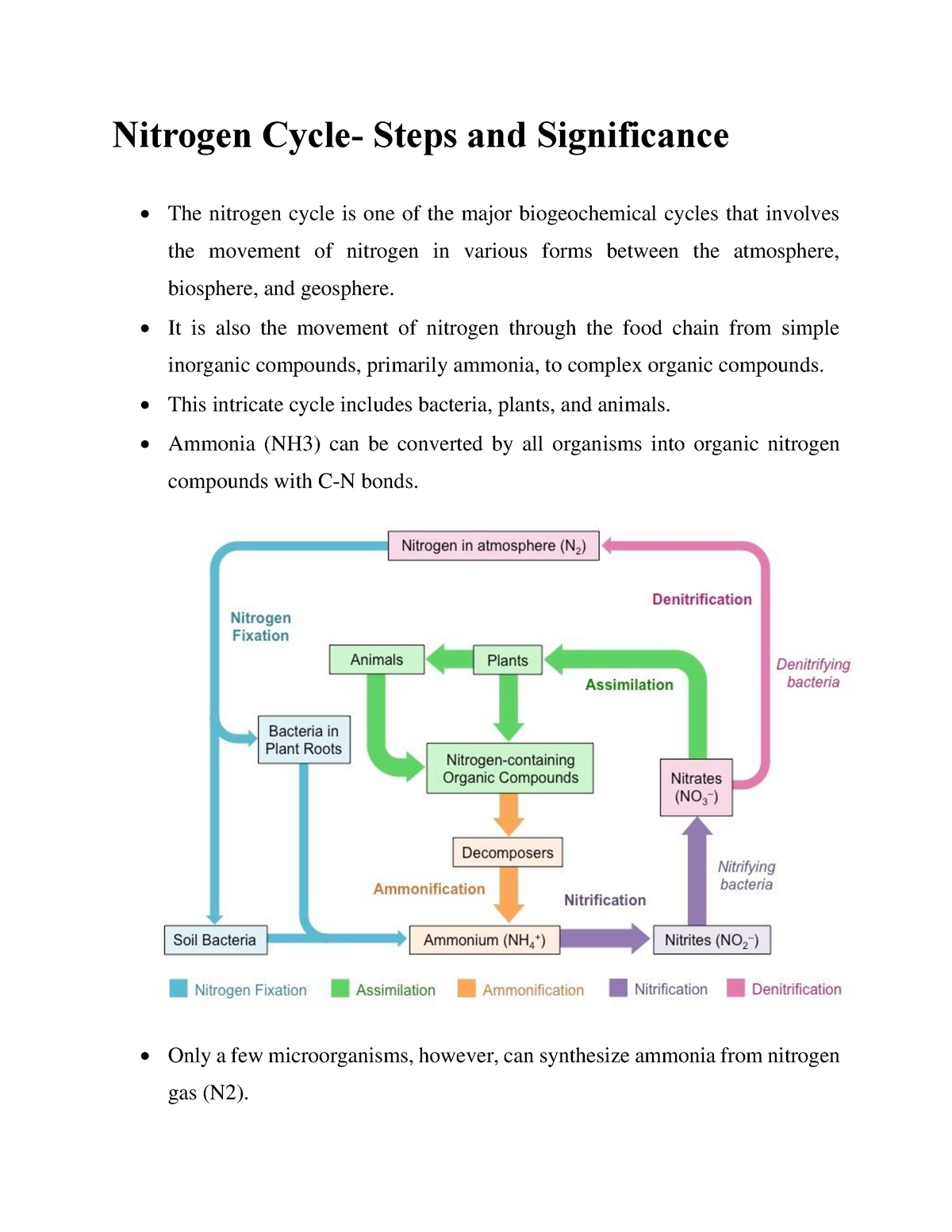
The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins. The pilgrims had a difficult time growing or finding enough food to last Nitrogen is also key to the existence of ecosystems and food chains. Nitrogen forms about 78% of the air on Earth. But plants do not use nitrogen directly from the air. That is because nitrogen itself is unreactive, and cannot be used by green plants to make protein. The Nitrogen Cycle. 1. Nitrogen is introduced into the soil by
Definition, Stages and Importance Biology Diagrams
Food chain, its types and eg. are briefly mentioned in the article below. A food chain is like a line that shows who eats whom in nature, as animals and plants are linked because they eat each other. These decomposers help in the breaking of complex organic molecules into simpler substances, and release nitrogen (through the nitrogen cycle Food chains, the nitrogen cycle, and the carbon cycle are examples of these interactions. A food chain is the sequence of steps through which the process of energy transfer occurs in an ecosystem. All organisms need a continuous supply of energy. Energy flows throughan ecosystem in one direction— through foodchains. It may also be considered as the movement of nitrogen through the food chain from simple inorganic compounds, mainly ammonia, to complex organic compounds. This complex cycle involves bacteria, plants, and animals. like animals, depend entirely on organic nitrogen from their food. The next step in the nitrogen cycle is the assimilation of